(12894 products available)


































































































































































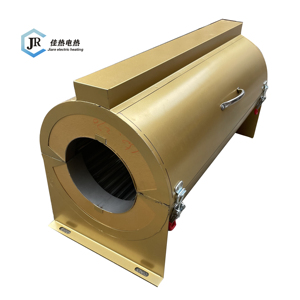





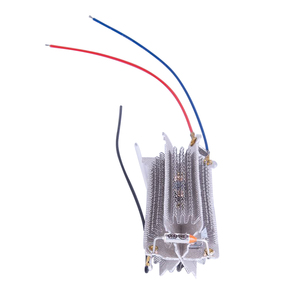


















































Industrial band heaters are typically used to heat the walls of barrels and tanks and are generally divided into two main categories: silicone rubber band heaters and ceramic band heaters.
The specifications of a band heater depend on the particular type and what it's made for. In general, they come in a range of power densities, often between 1 and 10 watts per square inch. Voltage usually varies between 12 and 480 volts with a standard of 120 volts, and the wattage power ranges from low to high depending on the temperature it will provide. The temperature of a band heater can go from a room to an extreme high of 1,000 °C or 1,832 °F. The size and thickness will vary depending on the individual application that it is used for.
A simple maintenance task that's required of these heaters is, of course, cleaning. They need to be cleaned throughout the day of any debris or spills to help them last longer. The surfaces need to be wiped down with any gentle cleanser or degreaser and dried thoroughly. Another task is to ensure that the fastening devices are checked periodically to ensure that they are not loose or damaged. Properly storing the heating bands in a dust-free and dry area will help them last longer. A storage space with a controlled room temperature and free from any debris or contaminants is advisable. Band heaters for barrels provided with insulation should be stored flat to prevent any distortion. Ideally, when not in use, the band heater for a barrel should be at room temperature. Keeping them out of cold storage will eliminate the need to heat them slowly to get them up to temperature.
As the global consumption of plastics continues to rise, the food industry is faced with new challenges regarding band heater uses. Efficient heating solutions are more critical than ever, driving the demand for electric band heater applications in various sectors.
Chemical industry
The chemical industry relies on tailored heating solutions to ensure smooth operations. Electric band heaters provide uniform heat for chemical processes, preventing product degradation and ensuring consistency. In the chemical industry, adaptability, precise control, and durability are paramount. Electric band heaters excel in meeting these demands, allowing for efficient and reliable heating in chemical applications.
Aerospace
In the aerospace sector, where safety and performance are paramount, electric band heaters offer reliable heating solutions. They provide consistent temperatures, reducing the risk of component failure and ensuring the integrity of critical aerospace systems. With their ability to withstand harsh environments and deliver uniform heat, electric band heaters are trusted tools supporting the aerospace industry's demanding standards. They find applications in areas such as component curing, de-icing systems, and fluid heating. Their precision, reliability, and versatility contribute to the efficiency and safety of aerospace operations.
Medical and pharmaceutical
In the medical and pharmaceutical fields, where temperature control and precision are crucial, electric band heaters play a significant role. They provide a stable heat source for equipment like sterilizers, incubators, and analyzers. Electric band heaters ensure reliable heating and support the quality and safety standards required in these sensitive industries. Electric band heaters offer a dependable heating solution, contributing to patient care and the advancement of medical technologies. They support the development and production of pharmaceutical products, medical devices, and research tools. Their ability to deliver consistent temperatures and adapt to specific needs enhances the efficiency and reliability of healthcare operations.
Food and drinks
In the food and beverage industry, where processing and production techniques require careful control of temperature and consistency, electric band heaters are indispensable. They ensure even heating of food products, preventing hot spots that can lead to overcooking or undercooking. Whether used in ovens, cookers, or processing equipment, electric band heaters contribute to the quality, safety, and efficiency of food and beverage manufacturing.
Energy and power
Electric band heaters provide reliable heating solutions in energy and power generation, supporting sustainable practices and efficient energy production. These versatile heaters find applications in renewable energy systems, oil and gas exploration, power generation facilities, and energy storage solutions. Their ability to deliver consistent and controlled heat contributes to the efficiency, safety, and sustainability of energy and power sector operations.
Applications
Depending on the industrial use, buyers must first ascertain the containers' size and shape, the materials' viscosity and composition, the heating environment and safety factors, and the energy efficiency and sustainability requirements. Also, batch versus continuous processes require distinct strategies. Regular assessments should be made to check if an upgrade is warranted.
Types
Selecting the proper band heater necessitates a thorough exploration of its many types. Firstly, buyers should study each model's operational principles to avoid any potential issues down the line. Secondly, when choosing, buyers must consider their furnace temperature range, watt density, materials, size and weight, energy source compatibility, power requirements, insulation characteristics, thermal cycling response, control and monitoring systems, electromagnetic interference, installation area, and environmental conditions.
Sizes
Band heaters come in a variety of sizes. Both the internal and external diameters of the heaters must correspond perfectly to the cylinders' dimensions to ensure a close fit. Buyers can use spacer shim rings for bespoke size requirements. One must remember that a too-loose fit can result in an uneven temperature distribution and a potentially dangerous situation.
Voltage
Voltage is an important feature when choosing a band heater. The voltage rating of the heater must equal the heater's supply voltage. Using a higher voltage heater than the supplied voltage can result in a potentially dangerous situation, while a mismatch can prevent the heater from reaching its intended temperature.
Wattage
This refers to the power output. It plays a crucial role in determining how quickly and effectively the heater can raise the temperature of the cylinder.
Construction Material
Buyers must also consider the band heater construction material. Stainless steel, aluminum, or brass offer varying levels of corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, so choose according to the application's specifics.
Control Method
Buyers must consider the control method for band heaters. The chosen heater should work seamlessly with the controllers, sensors, and feedback systems employed. It should be easy to link with the monitoring and control systems used in the process.
Q1: What are the current trends in industrial band heater technology?
A1: Recent developments include the shift toward energy-efficient heaters, the use of IoT for predictive maintenance, and the integration of energy-saving technologies like PID temperature control and SSRs. Besides, the need for environmental sustainability is driving the demand for low-energy consumption equipment, which has led to the popularity of ceramic band heaters and infrared band heater, both known for their energy efficiency and lower environmental impact.
Q2: How long can a band heater last when used properly?
A2: With proper usage and maintenance, such as controlling the temperature to avoid overheating and keeping it clean, the band heater can last 1-2 years or even longer.
Q3: What safety measures should B2B buyers consider when purchasing band heaters?
A3: Consider the safety features of the band heaters, such as over-temperature protection and grounding terminals. Also, invest in temperature controllers and thermal insulation to prevent heat loss and avoid surface burn hazards.
Q4: What is the ideal watt density for a band heater?
A4: The optimal watt density varies depending on the specific application and temperature required. Generally, it is between 1-3 watts/cm². For more precise calculations, consider the specific heat requirements of the materials in the particular application environment.