(6988 products available)
































































































































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship





 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship










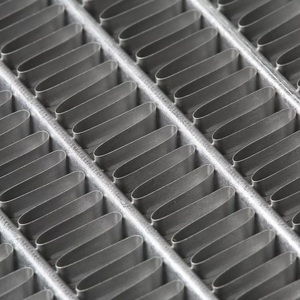
A brazed aluminum core is a heat exchanger made of aluminum that has been joined by brazing—a process that involves melting a filler alloy to create a bond between components. These cores are used in various applications, especially in heat exchangers like radiators and condensers, where aluminum's lightweight and corrosion-resistant properties are advantageous.
Brazed aluminum cores are primarily classified based on their application into the following types:
HVAC Brazed Aluminum Cores
The HVAC brazed aluminum cores are used in heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems. These systems are designed to control the temperature and air quality in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings. The HVAC systems rely on brazed aluminum heat exchangers to transfer heat efficiently, allowing for effective heating and cooling. The cores are lightweight, which is important for energy efficiency in these applications.
Automotive Brazed Aluminum Cores
These cores are used in automotive applications. They are designed to be part of the vehicle's cooling system, including radiators, intercoolers, and oil coolers. The automotive brazed aluminum cores are lightweight and have high thermal conductivity. This allows them to dissipate heat effectively, which prevents the engine or other components from overheating. The cores are also resistant to corrosion, which extends their lifespan in the automotive applications.
Refrigeration Brazed Aluminum Cores
These cores are commonly used in refrigeration systems. They are used in commercial and industrial refrigeration units, such as walk-in coolers, freezers, and large-scale refrigeration systems. The refrigeration aluminum cores are also used in food processing and storage facilities. They ensure that perishable goods are kept at the appropriate temperature. These cores are also used in heat pumps which provide heating and cooling in residential and commercial settings.
Power Generation Brazed Aluminum Cores
These cores are used in various ways in power generation facilities. For example, they are used in cooling systems for turbines, generators, and other critical equipment. The cores help to dissipate heat and keep these components operating at optimal temperatures. This ensures efficient power generation. Additionally, the aluminum cores are used in combined cycle power plants. They utilize waste heat from gas turbines to generate additional electricity.
Higher Strength:
Brazing is a process similar to welding that joins metals together using a filler alloy with a melting point above 450 °C but below the base metals' melting points. It creates very strong bonds between pieces of aluminum, making the whole core much stronger than if they were just glued or bolted together. A brazed aluminum core can better withstand high pressures, temperatures, and mechanical forces without leaking or falling apart.
Reduced Weight:
The strength of aluminum at a lighter weight makes a brazed aluminum core much more efficient. Aluminum cores are now used in applications like heat exchangers, radiators, and intercoolers where a lightweight but durable part is needed. Aircraft, automotive, and aerospace engineers can reduce overall weight while maintaining structural integrity and performance. This is especially important in transportation and cooling systems, where every pound counts.
Improved Thermal Conductivity:
Thermal conductivity allows heat to be transferred quickly from one side to another. It's measured in watts per meter per degree Kelvin (W/mK). The brazing process produces aluminum cores with improved thermal conductivity. The joints created by brazing form a metallurgical bond that is as good as or better than aluminum base metal. This leads to more efficient heat exchange in applications like radiators, air conditioners, and industrial cooling systems.
Enhanced Durability and Corrosion Resistance:
The brazing process creates a strong, permanent bond between aluminum pieces. This metallurgical bond is as strong as the aluminum itself, so it won't come apart or suffer from issues like galvanic corrosion that can affect welded or boled joints. The entire core is much more durable and long-lasting. It can withstand high pressures, temperatures, and repeated flexing or vibrations without leaking or failing.
Consider the Application
Different applications have different brazed aluminum core requirements. For example, if the core is for a high-performance heat exchanger, a core with a high strength-to-weight ratio may be needed. On the other hand, if the core is for an air conditioning unit, a core with good thermal conductivity may be sufficient. It is important to consider the application to determine the required specifications for the brazed aluminum core.
Evaluate the Thermal Conductivity
The primary function of a brazed aluminum core is to facilitate heat transfer. Therefore, cores made of aluminum alloys with high thermal conductivity, such as 1050 or 1100 aluminum, should be looked at. Cores with a thermal conductivity rating of 200 W/mK or more are good for most applications.
Assess the Structural Integrity
When choosing a brazed aluminum core, consider its strength and durability. This is more important for applications that expose the core to high pressures, temperatures, and harsh environments. Look for cores made from alloys known for their strength, like 6061 or 6063 aluminum. Also, consider the thickness of the walls and the core's design features, like reinforcements and flanges.
Examine the Weight
Sometimes, it is important to prioritize the aluminum core's weight. In applications like aerospace and automotive engineering, every extra kilogram can impact performance. In such cases, consider using aluminum cores made from lightweight alloys like 3003 or 5005. These alloys offer sufficient strength while minimizing weight.
Look at the Cost
While performance is important, the brazed aluminum core's cost also needs to be considered. If the application has a tight budget, it may be more economical to choose a core that meets the minimum requirements instead of going for the highest performance option. Consider the life cycle costs, which include initial costs, maintenance, and replacement. A cheaper core may have a lower upfront cost but could require more maintenance or have a shorter lifespan.
Q1: What are the sizes of brazed aluminum cores?
A1: There is no standard size for a brazed aluminum core. Various sizes and models are available to suit specific applications. Buyers can also get custom-sized cores to meet their specifications.
Q2: What is the core's working temperature?
A2: Aluminum cores can work at temperatures as high as 500 degrees Fahrenheit. However, the exact temperature depends on the type of core and application.
Q3: What is the core's lifespan?
A3: With proper care and maintenance, the brazed aluminum core can last for decades. It is durable and can withstand harsh conditions and high temperatures.