(11157 products available)



























































































































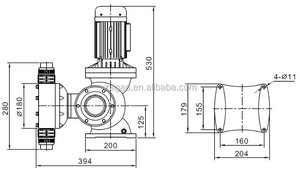












































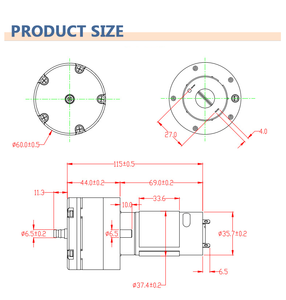






The type of diaphragm 6 that an incoming buyer selects depends on several factors, including application, usage, and compatibility. Diaphragm types differ by material, manufacturing process, or configuration. Here are some common diaphragm types.
Natural rubber is used in making some of the most cost-effective yet durable diaphragms. Its high elasticity and tensile strength make it suitable for fuel, oil, water, and gas applications. However, natural rubber is not used in applications with high temperatures or certain chemical exposures.
Nitrile, also called acrylonitrile butadiene rubber, is ideal for 6 diagraph applications that require resistance to oils and fuels. It is especially suited for the automotive industry, as it can watch out for petroleum-based products. Nitrile diaphragms are also largely used in Pnuematic Hydraulics.
Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer is a synthetic rubber resistant to oxidation, UV light, and weathering. Such features make the compound great for outdoor applications and areas prone to extreme environmental changes. It also withstands steam and hot water, better than most natural and synthetic rubbers.
PTFE is a chemically resistant plastic that forms a diaphragm with excellent barrier properties against corrosive chemicals. Other than that, it can also tolerate high temperatures. It is used in chemical processing industries and other extreme environments that break down other materials.
Buna-N, or Nitrile, offers great elasticity and resistance to petroleum-based products. That makes it suitable for oil and gas industry operations, but not so much outside. Its resistance to water, oxygen, and other non-petroleum chemicals is poor, which limits this rubber's feature in certain 6 diaphragm applications.
This thermoplastic elastomer combines rubber-like performance with plastic's ease of processing. Santoprene is enjoyed for its durability, elasticity, and resistance to temperature extremes and chemicals. Such features make it great for industrial applications and automotive components.
Diaphragm pumps are widely used in many industries. This is because of their efficiency in pumping both liquids and gases. The 6 diaphragm fits many pump types, serving diverse applications. Here is a rundown of these industries and how the diaphragms serve them.
Diaphragm pumps are relied on for their ability to handle corrosive chemicals with precision. The 6 Edpm diaphram is a variation preferred in this industry due to its resistance to chemical reactions and degradation, ensuring a longer pump life, as well as improved safety. These attributes reduce further the risk of leaks and contamination.
Diaphragm pumps with this diaphragm are useful in both water supply processing as well as wastewater treatment. It then transfers slurries, chemicals and other necessary water treatment solutions. These pumps are valued for their ability to operate reliably, despite irregularities in viscosity and particle content.
Expanding food and beverage processing and adhering to safety norms means the food and beverage industry has to continually observe hygienic practices. The diaphragm pump is used here because of its non-invasive pumping technique, ideal for transferring delicate materials like liquids and purees.
The petrochemical industry handles various viscous liquids, including oil and gas. Diaphragm pumps are particularly useful for transferring hazardous substances in environments requiring superior sealing. The 6 rubber diaphragm can survive harsh operating environments, making it ideal for this tough application.
PTFE diaphragms are preferred in this industry owing to their chemical resistance and non-porosity attributes, which are essential for maintaining the pure quality of meds. Diaphragm pumps in pharma help in the transfer of active ingredients, excipients, and other sensitive compounds whilst ensuring integrity is maintained.
In mining, these pumps transfer slurries and suspensions, balancing solid-liquid mixtures with uneven consistencies. In agriculture, they help to • irrigate and apply pesticides and fertilizers uniformly. Both industries appreciate the pumps' ability to work reliably in hostile conditions while managing non-Newtonian fluids with variable viscosities.
6 printer dium are made of various materials. They include PTFE, rubber, and the likes. Each of them has its unique features that make the diaphragm more useful than in other applications.
Material Composition
Apart from the types and industrial applicability of the 6 diaphram (six diaphragm pumps), its effectiveness in different applications depends on its material composition. These materials include rubber, PTFE, and others, each with unique attributes relevant for operating under inconsistent fluid conditions.
Diaphragm Design
6 diaphragms have different designs suited for different pumps and industries. Some of these designs are often molded-in composite fabrics for increased strength and better resistance to tearing in high-stress conditions. Others are flexible and move smoothly in response to pressure changes, allowing the effective pumping of fluids with variable viscosities.
Compatibility
Diaphragms are selected based on the fluid to be pumped and the operating condion. For example, a Buna N 6 diaphragm is perfect for petroleum-based fluids. At the same time, EPDM diaphragm pumps are excellent for hot, steam, and chemically active liquids.
Viscosity Handling Capability
The most important function of a diaphragm is to gently pump fluids whose viscosity may vary. The flexibility and tensile strength of the material determine the viscosity: the higher the viscosity, the tougher the material.
Preparation
Installing a diaphragm needs one to first ensure the pump housing is clean and free of debris, as well as the old diaphragm if there was ever any. One must carefully examine the pump for damage and make the required repairs before installing a new one, as its efficiency may be affected by a faulty—strong, weak—part.
Placing the Diaphragm
Gently place the new diaphragm in the designated mounting point in the pump. If there is a molded or pre-stressed section of the diaphragm, one should ensure it is facing the right direction as given in the manufacturer instructions. Ensure that the diaphragm sits evenly and there are no creases or bubbles.
Securing the Diaphragm
In this step, the manufacturer housing cover must be replaced gently to avoid disturbing the diaphragm. After that, the fasteners should be a bit tightened in a clockwise direction to secure the diaphragm properly. In this stage, it is crucial not to overtighten, as that may damage the diaphragm.
Testing the Installation
To wrap up the installation, turn on the pump and observe if it operates properly and efficiently. Carefully monitor for leaks or unusual noise. The pump should be running smoothly and without straining. If there are no signs of running smoothly, recheck to see if the diaphragm was probably installed.
Regular Inspection and Cleaning
One must regularly inspect and clean the diaphragm as well as related pump components to ensure long-lasting functionality. Depending on usage and environment factors, such inspections can range from weekly to monthly. The external part should be cleaned, while the internal one should be inspected for damage like tears, cracks, or wear.
Monitoring Performance
Closely observing the pump's functioning is critical in early damage detection so that necessary steps are taken. Symptoms like decreased flow, strange sounds, or fluctuating pressure are indicators of possible diaphragm problems. One must also continue monitoring pump efficiency to avoid additional damage and costly repairs.
Temperature and Pressure Maintenance
Overpressure and overtemperature are factors that may cause diaphragm failure, so it is important to operate the pump within its allowed limits. Proper monitoring equipment usage helps ensure the diaphragm does not experience extreme pressure or temperature spikes.
Material Compatibility
Using the right diaphragm for the pumped fluid is key to its longevity. One must ensure that the diaphragm material is compatible with the fluid. If the 6 printable material is chemically attacked, it will weaken the diaphragm, resulting in failure. Make sure to change the material when the operational fluide changes.
Repair or Replacement
Apart from regular maintenance, repair or replacement of the diaphragm will be needed eventually. Depending on the level of wear and tear, some diaphragms can be easily repaired. However, those that have reached their lifespan must be replaced to maintain pump efficacy. Don't forget to keep a spare 6 diaphragm on standby.
Proper Handling
As fragile as they may seem, 6 diaphragms demand cautious handling. Being careless can lead to undesired results such as cracks or tears, deteriorating the material's integrity and making it unusable. Therefore, use safety precautions, including gloves and goggles, when handling certain chemicals and substances that may cause harm.
Equipment Inspection
For safety and the sake of profitability, it is important to examine the diaphragm pump to ensure all components are in their proper working condition. This inspection helps identify worn or damaged components early enough to prevent accidents and pump failure down the line. Don't wait till the last minute to conduct these inspections; make them routine.
Pressure Regulations
One of the most important considerations is not to exceed the recommended pressure limits of the pump. Doing so may result in diaphragm rupture, which comes with hazardous splashes and spray of the pumped fluid. Ri ensure that pressure levels are monitored and controlled throughout operation.
Proper Ventilation
If the fluid being pumped through the diaphragm is volatile, ensure there is adequate ventilation in the area. These fluids can generate flammable vapors, and working in a space without proper air circulation can expose one to serious combustion risks.
Emergency Protocols
There must be emergency measures or protocols established in case of pump failure or leak. These emergencies may involve exposure to dangerous fluids. Know the nearest emergency equipment, such as showers, eyewash stations, and fire extinguishers, and be sure to have them within arm's reach whenever the need arises.
A1. In simple terms, a 6 diaphragm is a pump part mainly used in diaphragm pumps. It is used to separate two sides of the pump chamber and then create a seal. Diaphragms, on the other hand, come in various forms and are mostly used depending on the pumped fluid and the condition in which the pump operates.
A2. These 6 printer diaphams are made of rubber and other materials. They include PTFE, natural rubber, EPDM, nitrile, or Buna-N, and Santoprene. All of these materials offer a wide range of flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, making them suitable for pumping fluid.
A3. A diaphragm pump works by using flexible membranes or diaphragms to create alternating cavities within the pump chamber. One diaphragm side contracts while the other expands, causing the fluid to move from one chamber to another. This process is called suction and discharge, and it helps the pump efficiently move fluids through the inlet and outlet.
A4. Yes, there are certainly safety concerns when using this pump. Always keep an eye on the pressure levels because excess pressure can cause diaphragm failure, resulting in hazardous fluid spray and leakage. Employ emergency protocols in case of pump failure or leakage and ensure that the area is well ventilated, especially when working with flammable substances.