(697 products available)










































































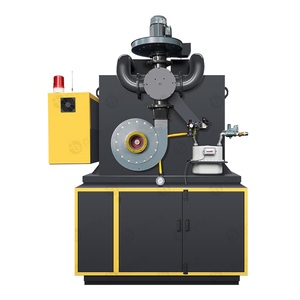









































































































A gas-fired crucible furnace melts a wide range of metals. They are preferred in places that electricity supply is an issue and where operational costs need to be reduced. Known for their ability to provide high-temperature heats, these furnaces are essential in various sectors. Therefore, understanding the different kinds of crucible furnaces is important for investment planning and future profitability.
These furnaces come in several configurations. For instance, some types have a crucible that is open, while in others, the crucible is tight. The high-pressure furnace uses more gas and is for melting large-volume materials. On the other hand, the low-pressure one consumes less gas and is ideal for small-scale operations.
They are also available in manual and automatic types. The automation level is convenient depending on the user's operational requirements. Automatic furnaces improve production due to their capacity for constant heat control and melting without frequent operator checks.
Gas crucible furnaces are essential tools in many industrial settings. The following are the commonly used metalworking applications:
The versatility in melting capacity and mobility make gas crucible furnaces ideal for remote foundries without electricity. They are essential for many manufacturers, especially for those who do casting or alloy making.
To select the right crucible furnace, buyers need to know the features, specs, and quality key factors of these furnaces. The gas-fired crucible's main features and specifications include the following:
Use the following tips and advice to help buyers stock quality gas-fired crucible furnaces:
Natural and propane gases are often the types used in gas furnaces. Propane is suitable for remote locations. It forges communities that lack direct access to natural gas lines. Propane can also be an economical option when the price is lower than natural gas. Natural gas is ideal for large-scale operations because it is cheaper and easier to access.
The furnace's maximum heat output determines how well it melts dense metals. Operating large-volume melting jobs requires a high heat. On the other hand, smaller crucibles do not need much melting heat. Therefore, choose a furnace with the right heat output for the melting tasks.
This factor involves considering both the crucible size and the overall furnace size. A big crucible is for large metal pieces or big batches. Small crucibles are for melting small metal quantities. A larger furnace requires more room, while the smaller one needs minimal space. This factor, however, can be crucial when space optimization is the main concern.
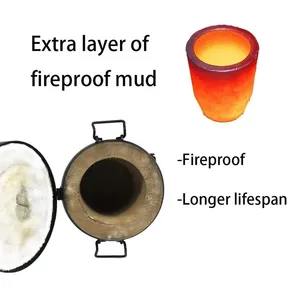
Select furnaces made of robust materials. They are better for harsh industrial environments. Such furnaces also have longer life spans and require fewer repairs. Consider whether the furnace is portable or permanent. Mobility is suitable for melting processes that frequently change locations.
Basic models require operators to monitor and adjust them constantly. Advanced ones automate the melting process by automatically configuring the set condition. The right choice for the user between these two types relies on labor availability and whether consistency is a primary goal.
With proper care and maintenance, gas crucible furnaces work best for many years. To achieve this, buyers should consider the following maintenance tips:
The furnace should only be heated and cooled slowly. Doing this prevents metal warping and cracking. Abruptly cooling or heating the furnace leads to thermal shock. It also weakens the furnace structure due to the internal material lining's temperature differences.
Do not use any reactive or acidic chemical substances to clean the furnace. These chemicals erode the crucible material and furnace linings. They may also cause unexpected fires, damaging the equipment further. Use only the recommended cleaning substances.
Ensure the work area around the furnace is well ventilated. Poor ventilation causes gas accumulation, leading to fire or explosions. Inadequate airflow also causes overheating of the furnace. Some gases can also cause harm to workers around if trapped.
Always repair the furnace using replacement parts from the original manufacturer. Non-genuine parts affect performance. It may also void the warranty if the gas furnace has one. In addition, local blacksmiths or a factory blacksmith should only make repairs to the furnace. This factor is because they have a better understanding of the structure more than other repairers.
Yes, these furnaces are ideal for operations that do not have electricity. They also work well for metals with low to medium melting points, such as aluminum, brass, bronze, and gold.
The operator should always put on personal protective equipment. Equipment such as gloves, safety glasses, and heat-resistant clothing protects one from burn injuries, flying metal, and extreme furnace heat. There should also be safety measures to prevent explosions and gas accumulation. They include proper ventilation and regular gas leaks checks.
Yes, these furnaces are portable and ideal for outdoor use. However, the outdoor environment should be safe for operation. Dangerous outdoor environments expose the furnace to damage or interference with its operations.
One crucial regulation is ensuring the gas supply system complies with local safety standards to prevent leaks and explosions. The other is having proper waste management systems for metal fumes and emissions to avoid environmental pollution.
These furnaces use either natural or propane gas. Natural gas is easily accessible in large quantities, while propane is more affordable where electricity is not readily available.