(46707 products available)



































































































































































































































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship

















Different types of PE waste recycling plants are available on the market, with varying capacities to suit different business needs. Many companies use the capacity and function of the recycling machine as the primary basis for selection.
By capacity:
Recycling plant capacities range from 100 kg per hour to over 5 tons per hour. Large-scale recycling plants are ideal choices for countries or businesses that deal with large volumes of waste plastic. Conversely, small- or mid-sized plants might better suit start-up businesses.
By function:
Some recycling plants only focus on the primary processing stage, while others offer more comprehensive services.
Washing recycling plants are mainly used to sort and wash waste plastic to remove impurities such as dirt and labels. The main equipment includes sorting machines, washing tanks, and centrifugal dryers.
Complete recycling plants include the washing process and further granulation to produce plastic pellets. Granulation will increase the value of the customers' final products and may also help the customers run a more profitable business. The advanced recycling plant also includes the blow mold and injection mold, which can create new plastic products directly from the recycled plastic materials.
The complete recycling plant consists of shredding, washing, and granulating processes. It can produce plastic pellets ready for further processing to create new plastic products. Key equipment includes shredder, washer, granulator, and extruder.
The key specifications of a PE waste recycling plant along with their corresponding maintenance tips are as follows:
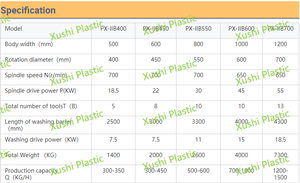
Capacity
Typically expressed in tons per hour, the capacity of the plant indicates the amount of plastic waste it can process within an hour. The higher the capacity, the more volume of plastic waste can be dealt with to produce more end products. As such, it is critical to ensure that the components of the plant that are responsible for its processing capacity, such as the feeder, shredder, separator, extractor, granulator, and compressor, are in good operational condition.
Power
Often indicated in kilowatts (kW) or horsepowers (HP), power signifies the amount of energy the plant requires to operate. This parameter is vital to ensure proper handling of the waste and production of recyclables. Machines such as motors and crushers should be inspected frequently so that no energy demand goes unmet.
Waste sorting system
All the mechanical parts of the sorting system, feeders, shredders, sink-float separators, extruders, blowers, vibrating screens, magnets, optical sorters, etc., should be checked and cleaned regularly so that items like mist filters, clutch drives, stator filters and rotary air valves don't become obstacles in correctly identifying and sorting out plastic wastes.
Crushing and washing system
Proper maintenance of the identifying and sorting out plastic wastes, such as the seals and blades of the washer and shredder, will help preserve the quality of the processed waste. Using them as per the instructions will also maximize their lifespan.
Control system
The control system is the electronic brain that governs the functions of the recycling plant. It needs to be protected from elements like rain and dust, which could affect its proper operations, by housing it in a well-screened enclosure. Moreover, its software should be updated on a routine basis, and all its sensors and cables should be checked periodically so that any anomalies can be quickly resolved before they turn into major issues.
Final product quality
The main purpose of a recycling machine is to enhance the quality of the plastic it creates from waste. Using original spare parts during repairs and taking proper care of its components ensures that the end products will meet the prescribed standards.
The PE waste recycling plant performs different tasks at each stage of the waste recycling process. It handles more varied types of waste because of its specialized equipment, which reduces, separates, and converts them into reusable raw materials. This flexibility makes it appropriate for a wide range of industries.
More than just plastic is dealt with by recycling facilities. Plants can take paper manufacturing leftovers, such as plastic-coated and non-plastic-coated cardboard, as well as other non-plastic packaging materials, like films and labels. The recycling process transforms plastic waste from being a limited resource into a significant one. The more types of waste the plant can handle, the greater the varieties of plastics that can be recycled, and the higher the environmental benefits.
Industries that frequently invest in PE recycling plants include the following:
Food and Beverage Industry
Industries that produce goods come in PE containers. They want to ensure their packaging is appropriate and disposable, therefore, they invest in bottle-to-bottle recycling facilities. These facilities enable them to use recycled content in their packaging, secure their supply of recycled materials, and meet consumer demands for sustainable practices.
Consumer Goods Manufacturers
Producers of goods that use PE as a primary component, like shampoo bottles and household product containers. They may have their own recycling facilities on-site or collaborate with centralized facilities to collect and process their containers. By investing in recycling plants, they can reduce their reliance on virgin plastic, lower production costs, and contribute to a circular economy where their products are recycled and reused.
Retail Sector
Retailers, especially large grocery chains and department stores, generate significant amounts of plastic film, bags, and packaging materials. To manage this waste efficiently and sustainably, many retailers are investing in recycling facilities located near or within their stores. By recycling onsite or nearby, they can reduce the volume of plastic sent to landfills, decrease transportation costs associated with sending waste to external facilities, and provide immediate value by converting waste into a usable product.
Logistics and Distribution Centers
Companies involved in handling, packaging, and distributing goods often rely on plastic containers, pallets, and packaging materials. These items are typically made from durable plastics that can withstand multiple uses. Logistics companies are increasingly installing recycling plants to manage the plastic waste generated in their operations. By recycling on-site or nearby, they can recover valuable materials like PET and HDPE used in their plastic containers and reduce the environmental impact of their supply chains.
Business needs assessment
Firstly, determine the business's objectives regarding plastic waste recycling. Identify the types of plastics to be recycled, the expected processing capacity, and the desired end products. This evaluation will help to align requirements with the available recycling plant options.
Technology and process exploration
Research the different technologies and processes employed in PE waste recycling plants. Understand the distinction between mechanical recycling and advanced recycling methods. Mechanical recycling involves sorting, washing, shredding, and melting plastic waste, while advanced recycling may include chemical or biological processes. Familiarize with the specific techniques utilized within these categories, such as single-stream vs. multi-stream recycling, and different approaches to separation, purification, and transformation of plastics.
Plant scale and capacity estimation
Consider the appropriate scale and capacity of the recycling plant based on the business's anticipated plastic waste volume. Small-scale batch plants may suit businesses generating limited plastic waste, while larger continuous processing plants are more suitable for handling significant quantities of recycled materials.
Efficiency and productivity comparison
When weighing different plant models, pay attention to their processing effectiveness and productivity. Check the sorting, washing, shredding, and extrusion efficiency of each step. Take into account factors like energy consumption, operating speed, and equipment performance to select the plant that can maximize processing capability.
Compliance with environmental standards
Ensure that the chosen recycling plant complies with the necessary environmental regulations and standards. Check if it possesses the required permits and certifications to operate legally. Verify its adherence to environmental guidelines to minimize pollution and promote sustainable practices.
Cost and return on investment analysis
Consider the upfront costs, operational expenses, and potential revenue generated from recycling. Evaluate the return on investment by estimating the financial impact of the recycling plant on the business.
Q1: What are the latest technologies used in PE waste recycling plants?
A1: The latest PE recycling technologies include advanced sorting and separation systems, chemical recycling, and closing loop washing and recycling plants.
Q2: What is the future trend of PE recycling plants?
A2: The future trends will probably focus on chemical recycling, integrated waste management systems, and AI.
Q3: What is the role of additives in enhancing PE waste recycling?
A3: Additives can improve the quality of recycled PE by enhancing its physical properties, making it suitable for various applications.
Q4: What are the challenges in handling different grades of PE waste in recycling plants?
A4: The challenges include sorting difficulties, variations in quality, compatibility with recycling technologies, and economic factors.
Q5: What is the impact of recycled PE on the sustainability of product manufacturing?
A5: The use of recycled PE reduces the demand for virgin plastic, lowers environmental impact, and contributes to a circular economy.