(454 products available)































































































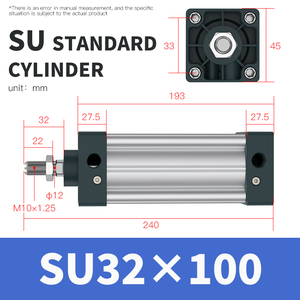

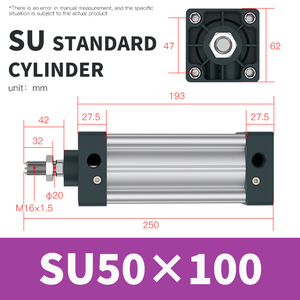










































































































There are various types of SU pneumatic cylinders available that perform distinct functions using the same general principles. The following table outlines some of the typical types of pneumatic cylinders:
Conveyor belt:
Pneumatic conveying systems mainly rely on the power of air pressure and suction to move materials along with belts by using pneumatic cylinders to create airflow. This airflow moves the goods through a process known as aeration, where items are placed on a perforated plate and supplied with air until they float and can easily be moved along the system. This method not only efficiently conveys materials but also reduces friction and energy consumption.
Robots:
Pneumatic SU cylinders are often found in the field of robotics. They can be used to adjust or move various parts of the robot. For instance, they can be employed for the adjustment of height or the opening and closing of clamps or grips. Robots equipped with pneumatic cylinders can be utilized in many different industries for purposes like assembly, picking, and putting, as well as for the handling of materials.
Packaging:
Pneumatic cylinders are widely used in the packaging industry. They are employed in procedures like sealing, labeling, bottling, and filling. For example, bottling lines can make use of SU cylinders to rapidly and accurately position containers, ensuring that they are capped and labeled correctly. Moreover, the cylinders can also be utilized for the packing of products into boxes or bags and for the sealing operations.
The automotive industry:
Cylinders are common pneumatic devices used in the automotive industry for assembly line production. As the main power source responsible for pushing, pulling, and rotating parts, they efficiently handle heavy-duty work. For example, SU cylinders can be used for the assembly of car bodies, the installation of parts like engines, or the clamping and fixing of workpieces. Their fast operating speed can greatly enhance production efficiency.
Injection molding machines:
The core working mechanism of a pneumatic injection molding machine lies in its molding. This means that the shape of workpieces will be altered. For this reason, molds will have to be opened and closed as well as adjusted and positioned.
The following suggestions may assist microbusinesses and huge industrial sectors in selecting the proper SU cylinder for their needs.
Analyze application needs
Determine the intended use by taking into account factors such as load weight, speed requirement, stroke length, and operating environment. Select a cylinder designed for high-temperature places, for example, if it will be exposed to high temperatures or contaminated with dust and chemicals.
Evaluate force and pressure
The output force of the cylinder depends on the load weight and the pressure. Select an appropriate pressure and calculate a suitable cylinder size to generate the necessary force. The pressure is measured in pascals (N/m²), and the area of the piston is in meters squared.
Think about the mounting style
Mounting types that are commonly used are fixed, trunnion, tied, and slotted mount. Decide how to install the cylinder to the other parts and choose a cylinder with an appropriate mounting style.
Choose an appropriate stroke length
A stroke length that matches the required moving distance in the application should be selected. For some applications, if the required moving distance is beyond the available stroke lengths, multiple cylinders or a cylinder with a longer stroke length may be used.
Consider selecting a rod or a non-rod
In applications that need compact design, a rodless cylinder with a sliding carriage can be used. It is also called a non-rod. For cost-effective solutions, consider cylinders with different piston rod materials and coatings.
Choose an actuating type
A double-acting cylinder is one that moves fluid power in both extending and retracting phases; a single-acting cylinder is one that only uses internal springs to make it retract. Both options are relevant to specific applications, so consult with engineers to better comply with design needs.
Q1: What is the difference between a SU cylinder and a standard SU cylinder?
A1: The main difference between standard and non-standard SU pneumatic cylinders is their size and shape. Standard cylinders will have set dimensions, while non-standard or custom-made cylinders can be manufactured to a specific size or with a particular feature.
Q2: How does a SU rodless cylinder work?
A2: A rodless cylinder works by moving a load along its length. This is done by using a magnetic strip attached to the moving part of the cylinder and a static part that contains the pneumatically powered element. In this case, the SU element will drive the load along the length of the cylinder.
Q3: How long do pneumatic cylinders last?
A3: Depending on usage, combined factors, like the material of the cylinder and whether it has been lubricated or not, cylinders can last anywhere from two to twenty years. However, some factors may cause the cylinder to fail faster, like corrosion or not using the right lubrication.
Q4: What are the main types of SU cylinder?
A4: The main types are tie rod, sleeve, unclod, and non-contact cylinders. The most common of these is the tie rod as it is more durable and offers a better performance.